Current Source#
Current Source = {model_name} <optional integer> <float_list> [E/M]
Description / Usage#
This card is used to specify the model for the source term on the voltage potential equation. Values for the permissible {model_names} and the associated <optional integer> and <floatlist> parameters are given below.
{model_name} |
Name of the model for the source term on the voltage equation having permissible values
|
<optional integer> |
This is required for the BUTLER_VOLMER model only. |
<float_list> |
One or more floating point numbers (<float1> through <floatn>) whose values are determined by the selection for {model_name}. Note that not all models have a <float_list>. |
Source-term model choices and their parameters are discussed below. WARNING: make sure the equation term multipliers for the source terms are set to unity (see the Equation Cards segment in the previous chapter).
CONSTANT <float1> |
For the CONSTANT current source term, there is a single input parameter corresponding to the current density.
|
USER <float_list> |
For a user-defined model, the set of parameters specified in the <floatlist> are defined in file user_mp.c in the function usr_current_source. |
BUTLER_VOLMER <integer> <float1> <float2> <float3> <float4> <float5> <float6> <float7> <float8> |
This is the homogeneous current source or sink term (in units of amphere per unit volume, e.g. A/cm3) as described by the Butler-Volmer kinetic model (see the Theory section below).One integer and 8 flotas are required:
|
ELECTRODE_KINETICS |
This is a toggle, turning the model on; no parameters are required. |
FICKIAN_CHARGED |
This is a toggle, turning the model on; no parameters are required. |
NET_CHARGE |
This is a toggle, turning the model on; no parameters are required. |
STEFAN_MAXWELL_CHARGED |
This is a toggle, turning the model on; no parameters are required. |
Examples#
Sample card for the CONSTANT model:
Current Source = CONSTANT 0.50
Sample card for the BUTLER_VOLMER model:
Current Source = BUTLER_VOLMER 0 1. 1000. 0.5 4.e-5 1. 1. 353. 0.
Technical Discussion#
The CONSTANT and USER models are those standardly available in Goma.
In the BUTLER_VOLMER model the current source or sink due to a homogeneuous electrochemical reaction involving a single species (e.g., the hydrogen oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions in a hydrogen-feuled polymer-electrolyte-membrane fuel cell) is computed using the Butler-Volmer kinetic model as described below in the Theory section.
In the FICKIAN_CHARGED model, current source or sink for electrochemical processes involving dilute electrolyte solution and multiple species as in LIGA electrodeposition is computed.
The NET_CHARGE model is used to compute the net charge or current source in a region where the concentrations of positively and negatively charged species differ as in the space layer of a atmospheric copper sulfidation process, in which the copper hole and vacancy concentrations differ such that charge separation occur (see the reference listed below in the Reference sub-section, Chen 2004, for further details).
In the STEFAN_MAXWELL_CHARGED and ELECTRODE_KINETICS models, current sources or sinks for electrochemical processes involving concentrated electrolyte solutions and multiple species as in thermal batteries are computed.
Further details of these models can be found in the SAND Reports and proceeding paper referenced below in the Theory sub-section.
Theory#
BUTLER_VOLMER model: for the Butler-Volmer kinetic model with the exchange current density being dependent on a single species is given by (cf. Newman 1991, Chen et al. 2000, Chen and Hickner 2006):
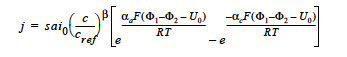
where j is the homogeneous current source or sink in units of A/cm3; s is the stoichiometric coefficient with a sign convention such that j represents a source when s > 0 and sink when s < 0; ai0 denotes the product of interfacial area per unit volume by exchange current density, which has units of A/cm3; c and cref are, respectively, species and reference molar concentrations in units of moles/cm3; β is reaction order; αa and αc are, respetively, the anodic and cathodic transfer coefficients; F is the Faraday’s constant ( ≡ 96487 C/mole) and R is the universal gasl constant ( ≡ 8.314 J/mole- K); Φ1 and Φ2 are, respectively, the electrode and electrolyte potentials in unit of V; U0 is the open-circuit potential in unit of V; and T is temperature in unit of K.
NET_CHARGE model: The net charge or current source in a region with charge separation (e.g., in a space charge layer in which hole and vacancy concentrations differ as in the atmospheric copper sulfidation corrosion process) is given by
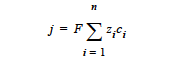
where j is the net charge or current source in units of A/cm3; zi is the charge number and ci is the molar concentration in units of moles/cm3, respectively, of species i; F is the Faraday’s constant ( ≡ 96487 C/mole); and n is the number of charge species present.
References#
Newman, Electrochemical Systems, 2nd Edition, Prentice-Hall, NJ (1991).
K. S. Chen, G. H. Evans, R. S. Larson, D. R. Noble, and W. G. Houf, “Final Report on LDRD Project: A Phenomenological Model for Multicomponent Transport with Simultaneous Electrochemical Reactions in Concentrated Solutions”, Sandia Report SAND2000-0207 (2000).
K. S. Chen and G. H. Evans, “Multi-dimensional Multi-species Modeling of Transient Electrodeposition in LIGA Microfabrication”, Sandia Report SAND2004-2864 (2004).
K. S. Chen, “Multi-dimensional Modeling of Atmospheric Copper-Sulfidation Corrosion on non-Planar Substrates”, Sandia Report SAND2004-5878 (2004).
K. S. Chen and M. A. Hickner, “Modeling PEM fuel cell performance using the finiteelement method and a fully-coupled implicit solution scheme via Newton’s technique”, in ASME Proceedings of FUELCELL2006-97032 (2006).
