Rel Gas Permeability#
Rel Gas Permeability = {model_name} <float> []
Description / Usage#
This card specifies the model for the relative gas phase permeability for flow in a partially saturated porous media, such that the gas flow is the pressure gradient in the gas times the permeability times the relative gas phase permeability divided by the gas viscosity. This card rests on a consistency in the specification of the relative liquid permeability (see models on the Rel Liq Permeability card) and this, the relative gas permeability. Definitions of the input parameters are as follows:
CONSTANT |
{model_name} for constant relative gas phase permeability with a single input value:
|
The CONSTANT model is rarely used, as it is dependent on the saturation level and the relative liquid permeability value. Please see the Rel Liq Permeability card.
SUM_TO_ONE |
{model_name} for the relative gas phase permeability. This model assumes that the relative liquid permeability and relative gas permeability add to one.
|
Examples#
Following is a sample card:
Rel Gas Permeability = SUM_TO_ONE 0.0001
This card specifies that the relative gas permeability in Darcy’s law for the gas flux is to depend on the liquid phase relative permeability such that the two sum-to-one. The gas viscosity here is specified to be 0.0001, in the appropriate viscosity units of M/L/t.
Technical Discussion#
This card is only required for Media Type POROUS_TWO_PHASE. Darcy’s law for gas flow is, in its simplest form:
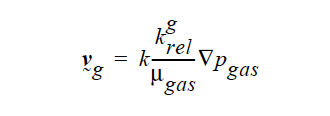
where, the Darcy velocity is proportional to the gradient in gas pressure, with k being the permeability, krelg being the relative gas permeability and μgas the viscosity of the gas. For the SUM_TO_ONE option above, the floating point constant is the gas phase viscosity, and the gas-phase relative permeability is calculated using

For the CONSTANT option the floating point constant must include the effect of viscosity, viz. the constant represents krelg/μgas
References#
GT-009.3: GOMA’s capabilities for partially saturated flow in porous media, September 1, 2002, P. R. Schunk
SAND96-2149: Drying in Deformable Partially-Saturated Porous Media: Sol-Gel Coatings, Cairncross, R. A., P. R. Schunk, K. S. Chen, S. S. Prakash, J. Samuel, A. J. Hurd and C. Brinker (September 1996)
