Solid Thermal Expansion#
Solid Thermal Expansion = {CONSTANT | SHRINKAGE} <float> [1/T]
Description / Usage#
This card is used to specify the model for thermal expansion of solid materials. Definitions of the input parameters are as follows:
CONSTANT |
Name of the model for the thermal expansion coefficient. |
SHRINKAGE |
Model for adding solidification shrinkage stress effects for enthalpy models. Experimental only (1/25/2013). |
<float> |
The value of the thermal expansion coefficient. For the SRINKAGE model this float is not used. |
Examples#
The following is a sample card:
Solid Thermal Expansion = CONSTANT 0.001
Technical Discussion#
When solid materials expand due to temperature changes, the strain field is composed of two components, the strain due to the stress field and the strain due to thermal expansion:
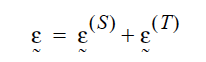
The strain due to thermal expansion is given by
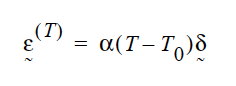
where \(\alpha\) is the linear thermal expansion coefficient \(T_0\) and is the reference temperature (see Solid Reference Temperature card). As a result, the solid constitutive relation contains an extra term:
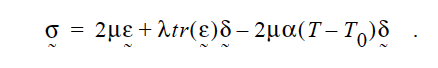
Note, the linear thermal expansion coefficient is presumed to be independent of strain and the Lame constants are presumed to be independent of temperature. (Model is hardwired right now in GOMA source, PRS 1/23/2013).
In the case of the SHRINKAGE model, an additional term is added on to the deviatoric stress:
References#
For a discussion of linear thermoelasticity, see (Section 6.2)
Malvern, L. E., 1969, Introduction to the Mechanics of a Continuous Medium, Prentice-Hall
