shell_filmp#
EQ = shell_filmp {Galerkin_wt} SHELL_FILMP {Interpol_fnc} <floatlist>
Description / Usage#
This card provides information for solving the film lubrication equation for free surface flow. Definitions of the input parameters are defined below. The Galerkin weight and the interpolation function must be set the same for the code to work properly. Counterparts to this equation for lubrication flow of capillary films (film-equations) are lup_p equation.
shell_filmp |
Name of equation to be solved. |
{Galerkin_wt} |
Two-or four-character value that defines the type of weighting function for this equation, where:
|
SHELL_FILMP |
Name of the variable associated with this equation. |
{Interpol_fnc} |
Two-or four-character value that defines the interpolation function for the variable SHELL_FILMP, where:
|
<float1> |
Multiplier for the mass matrix term. |
<float2> |
Multiplier for the advection term. It is not activated. |
<float3> |
Multiplier for the boundary term. It is not activated. |
<float4> |
Multiplier for the diffusion term. |
<float5> |
Multiplier for the source term. |
Examples#
Following is a sample card:
EQ = shell_filmp Q1 SHELL_FILMP Q1 1. 0. 0. 1. 1.
This applies the film flow equation with all terms activated.
Technical Discussion#
The equation solved is as follows:
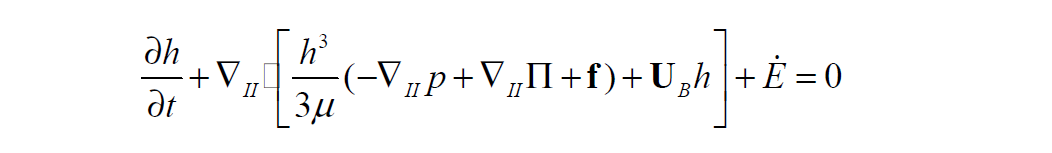
The mass matrix multiplier activates the time-derivative term.
The diffusion multiplier activates the terms inside the divergence operator and represents the flux or the flow rate of the liquid film.
The source (or sink, in this case,) activates the last term, rate of evaporation.
This equation has to be used with the equation describing SHELL_FILMH.
