Fickian Diffusivity#
Fickian Diffusivity = {model_name} <species> {float_list}
Description / Usage#
This card allows the user to select a Fickian diffusion mode when the model in the Diffusivity card is HYDRO. There are two {model_name} options for this mode; definitions of the input parameters are as follows:
ANISOTROPIC |
an anisotropic Fickian diffusion.
|
EXP_DECAY |
an exponential decay of flux.
|
Examples#
Following are two sample cards:
Fickian Diffusivity = ANISOTROPIC 0 2.e-6 2.e-6 0.
Fickian Diffusivity = EXP_DECAY 0 0.01 1.e-3
Technical Discussion#
In modeling suspension flow, often a sharp concentration gradient is encountered, and the numerical convergence becomes very poor. This card should be used for numerical stability (smooth out the wiggles) and should only be introduced as a last resort. The magnitudes should remain small relative to shear rate and viscosity diffusivities.
As the name implied, anisotropic Fickian diffusivity defines an additional flux contribution much like a classic Fickian diffusion term; i.e.,

If the exponential decay option is used, the flux vector has the form,
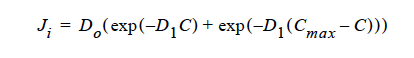
where C and Cmax are volume fractions of suspension locally and at maximum packing.
References#
No References.
